How to Create Accessible Apps for Android
Almost everyone has a smartphone. We use them for entertainment, communicating, exploring new locations, and paying for things. However, some people aren’t able to enjoy their full potential due to physical disabilities. For people with physical disabilities, developers have created special ways to interact with mobile devices.
Disabled people are using smartphones on a daily basis just like everyone else. However, they don’t use them the same way, and developers should take this into account when creating mobile apps. Adding accessibility to your mobile app is non-negotiable if people with disabilities are your target audience. Even if they aren’t, though, by adding accessibility features you can broaden your audience and help people who find using smartphones challenging.
A recent Google I/O presentation revealed many new technologies and Android apps for the disabled that will help people with access challenges use smartphone apps. We can see how much tech companies are actually doing to make apps accessible. The task of all developers is to create their apps with these technologies in mind according to mobile accessibility standards and guidelines.
Let’s talk about what accessibility applications technologies are currently available for developers and users.
Android accessibility technologies
The Google Accessibility team worked hard this year to develop applications for people with disabilities, and here we’ll talk about both new announcements and old applications from Google for making apps accessible.
Gboard
Google has designed a new feature for their virtual keyboard that allows users to access their devices using Morse code. Now people with physical challenges will be able to communicate with Morse code through a smartphone. For now this function is available in beta. Users have a possibility to customize the settings according to their needs.
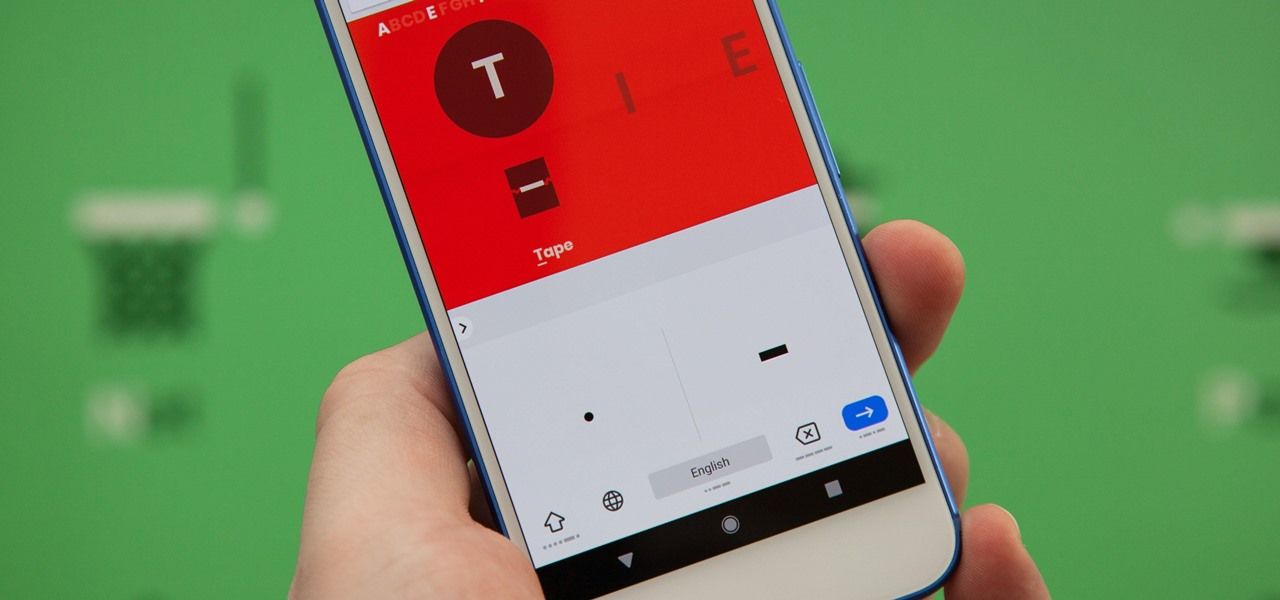
Gboard is compatible with Switch Access, that enables you to use Gboard with third-party devices. To make typing faster, Google took care about showing users suggested words above the keyboard.
Lookout
Lookout is an one of the apps for people with special needs that uses a smartphone’s camera to capture objects, signs or text around a user and then uses machine learning to identify the relevant objects. It is able to capture imagery in real time and tell the user what it’s seing. Lookout informs users about their location and the location of objects around them.

Lookout features several modes, for example, home, work and play. Lookout will pay attention to certain data it sees according to the mode. This feature works as a guide for users that can’t interrupt their activity with looking at the display. Lookout also enables users to control the device externally.
For example, you can use a fingerprint sensor to switch modes or cover the camera to pause the application. Lookout also works in offline mode.
Lookout will become available for U.S. users of Pixel devices in summer 2018. Android Oreo and Android P will support it.
Sound Amplifier
Sound Amplifier needs only your smartphone and a set of headphones to help you understand conversations in loud environments. It enhances relevant sounds and minimizes background noise. The interface of this application consists of two sliders – one for controlling the volume and another one for filters that eliminate background noise. There is also an “active listening” tool that allows to hear in a loud environment in real time and adjust the audio.
Sound Amplifier will be present in Android P, which is coming out very soon.
Select to Speak
This is one of the most impressive technologies; it allows users to select text right in the camera view without having to take a photo. However, it can select text in a photo as well. Select to Speak than reads the selected text out loud and highlights it.
Voice Access
Voice Access has been anticipated for a really long time, and it will finally become available for users in Android P. Voice Access helps people with physical disabilities control their smartphones with voice commands.
Currently Voice Access is in beta testing. It has the similar technology to Google Now, but there are way more available voice commands here. Google claims that this application will enable users with motor functions disabilities use Android devices. When you activate Voice Access, each element on the screen is assigned a number. A user can launch an app or press buttons by articulating a certain number. Besides, Voice Access also supports other commands like “open the browser”, “go to home page” or “scroll down”.
BrailleBack
BrailleBack works with TalkBack and helps blind users. It connects a Braille device to a smartphone via Bluetooth and presents the screen interface on the braille display. This allows a user to navigate the smartphone. Typing text is also easier for blind users with BrailleBack as they’re able to use a braille keyboard.

BrailleBack gives users a possibility to input information and enter text using a braille keyboard. You can download and install BrailleBack from Google Play. There you can also find information for developers that will help you build apps for the blind and add support of BrailleBack into your current app.
TalkBack
Google TalkBack is a mobile application that’s pre-installed on Android mobile phones. It articulates everything that’s happening on the screen and also voices the results of user actions. In this article, we’ll show you how to make applications that are able to use this service.
Google took care about making third-party mobile apps compatible with Google Talkback so developers don’t need to spend too much time to get things working. Let’s see what steps you should take to make your application accessible for people with disabilities.
How to create an accessible app with TalkBack
Step 1
In the XML layout, add an android:contentDescription attribute that will contain the component displayed on the screen. As most clickable elements don’t include text (e.g. Like, Share, and Favorite buttons.), it’s very important to mention this attribute. For dynamic components like Play/Pause, you need to use a setContentDescription() method.
Step 2
TalkBack reads text from the screen, which is why you need to assign text for the EditText component. You can assign an android:text attribute, but android:hint will be a better option. In this case you won’t need to assign the android:contentDescription attribute.
Step 3
Not all elements on the screen are clickable: some are purely visual, for example pictures. You’ll need to assign an android:focusable=”true” attribute so that TalkBack is able to articulate the contents of the contentDescription for such elements. Some people also use special devices to use an app, for example D-pads, trackballs, and keyboards. For these cases, it’s better to set the right order of transitions between components. For this, use the following attributes:
- nextFocusUp
- nextFocusDown
- nextFocusLeft
- nextFocusRight
- nextFocusForward
Step 4
Use scalable pixels when you set the font size. People with poor sight should be able to increase the font size on their own.
You should also remember to test your app with TalkBack as often as possible to ensure that everything works correctly.
Design tips
The designer has the biggest responsibility when it comes to developing accessible apps. There are several rules you should follow to design an app for disabled:
-
- Use recommended element sizes. This means that clickable elements should be at least 48×48 dp. The bigger they are, the better.
- Use as few time-dependent elements as possible. Time-dependent elements are those that disappear after a short period of time. For example, Play/Pause buttons that hide shortly after the video starts. Avoid such elements or think of an alternative.
- Design your app with larger fonts in mind.
- The hierarchy of elements is very important for users. They need to understand where they are in the app at any time, so you’ll need to think through a meaningful and clear architecture.
- To help people with color blindness, you shouldn’t rely solely on colors in your app’s design. For example, if you only change the button’s color when the input is incorrect, a user might not notice. It may look like the app simply doesn’t work. To avoid this situation, add text, different element shapes and sizes, or touch-based (haptic) feedback.Here are two examples of what can happen when you type the wrong name into the field. Which is clearer?

-
- Try to use high contrast colors for background and text. This will allow people with bad displays see the text more clearly. The recommended contrast ratio is 4.5:1.
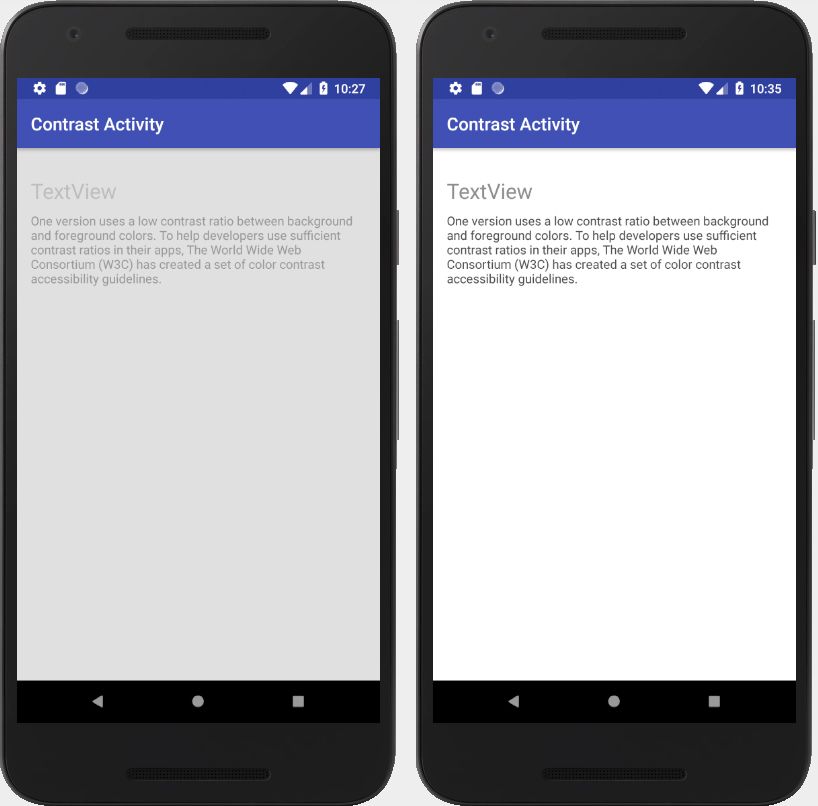
- The distance between interface elements should be at least 8 dp.
If you follow these design tips for accessible apps, you’ll be able to create an application that’s accessible for anyone.
Conclusion
Google TalkBack is one of the must-have services if you want to make apps for people with disabilities. People use technologies to make their lives easier, and disabled people shouldn’t be left out. Companies like Google make it really easy for developers to create accessible apps, and at Mobindustry we strongly support app accessibility.
If you want to adapt your app for everyone and increase accessibility, or if you want to create apps for disabled people specifically, contact us. Mobindustry provides accessibility app development consulting.
Article written by:
Vladislav Mykhalyk


